Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>


































 Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit! Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!  Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
> FcRn(Neonatal Fc Receptor) 
For a long time, IgG has been the only class of antibodies that are actively transferred from mother to offspring. This results in short-term passive immunity, and the specific IgG transport is accomplished by FcRn. In 1972, Jones et.al. first identified a receptor that transport maternal IgG to newborns in the gut of neonatal rats, hence after it was named as Neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn). FcRn expression during pregnancy and lactation plays a role in transporting IgG across the placental barrier and the intestinal tract. A variety of tissue cells can be detected throughout the life cycle. The main function is to maintain the level of IgG and albumin in the serum and regulate the distribution in the tissue.
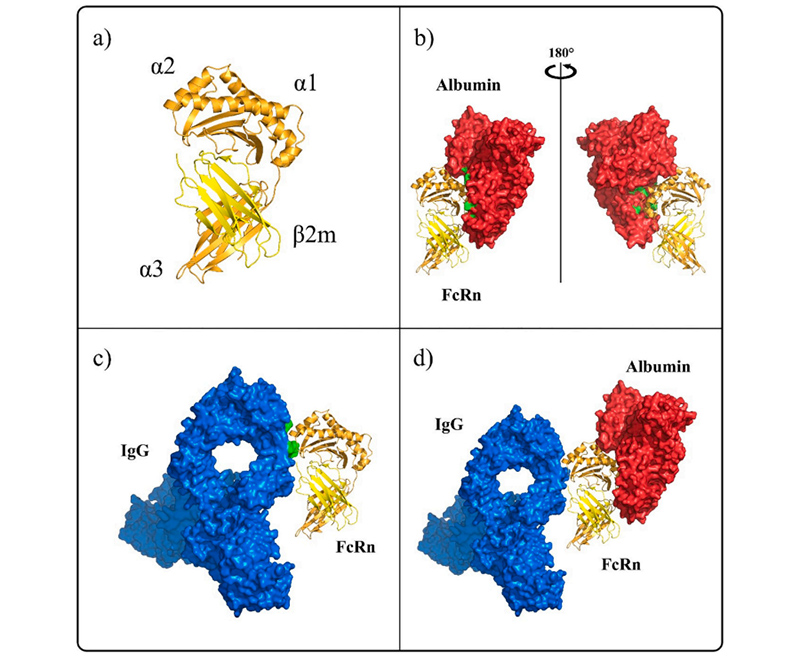 Human FcRn interaction with ligands IgG and albumin
Human FcRn interaction with ligands IgG and albuminFcRn is a heterodimer composed of two subunits, FCGRT and B2M. FCGRT has three extracellular functional regions including three soluble domains (α1, α2, and α3), a single transmembrane helix and a cytoplasmic tail (some studies showed the cytoplasmic tail region composed of 44 amino acid residues that may contain signals that mediate intracellular pathways). Its molecular weight is 40 to 50 kDa, called the α chain while the molecular weight of B2M is 14 kDa, called the β chain. The two chains are joining in the form of non-covalent bonds. FCGRT must be assembled with B2M to play a transport role. Studies have shown that the binding site of FcRn with IgG and serum albumin is not the same, so the binding of FcRn to IgG is not interfered by serum albumin.
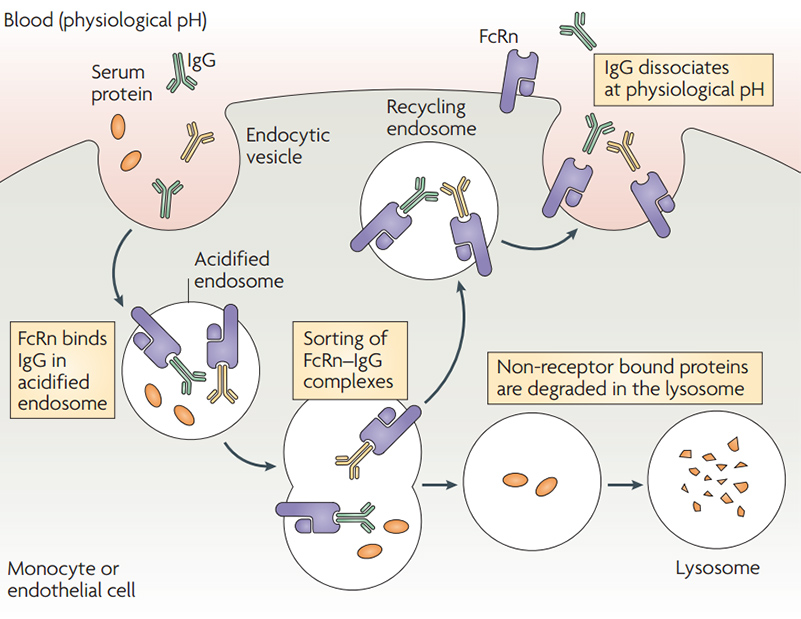 FcRn-mediated IgG and serum albumin recycling
FcRn-mediated IgG and serum albumin recycling![]() Expressed by HEK293 Cells: to realize post-translational glycosylation and other modifications and correct protein folding
Expressed by HEK293 Cells: to realize post-translational glycosylation and other modifications and correct protein folding
![]() Various species: Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque, Rat, Porcine, Rabbit, Feline, Bovine, can be fully applied to different cross species experiments
Various species: Human, Mouse, Cynomolgus/Rhesus macaque, Rat, Porcine, Rabbit, Feline, Bovine, can be fully applied to different cross species experiments
| more than 95% as verified by SDS-PAGE |
more than 90% as verified by SEC-MALS |
![]() Low endotoxin:<1.0 EU/µg
Low endotoxin:<1.0 EU/µg
![]() Biotinylated FcRn proteins labeled with AvitagTM offered. The labeling efficiency is high, and the labeling site is specific and clear, which is suitable for ELISA/SPR/BLI detection based on binding to streptavidin in the process of drug development and process optimization
Biotinylated FcRn proteins labeled with AvitagTM offered. The labeling efficiency is high, and the labeling site is specific and clear, which is suitable for ELISA/SPR/BLI detection based on binding to streptavidin in the process of drug development and process optimization
![]() Affinity verified by SPR & BLI: high-bioactivity guaranteed, and protocols offered free of charge
Affinity verified by SPR & BLI: high-bioactivity guaranteed, and protocols offered free of charge
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Host | Product Description | Structure |
|---|
Authors: Jones EA, Waldmann TA.
Authors:Derry C. Roopenian, Shreeram Akilesh.
Authors:Imke Rudnik-Jansen, Kenneth A. Howard.
Authors: Karissa L. Gable, Jeffrey T. Guptill.
> Learn more about ComboX, a combination of universal solutions
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.