
Leave message
Can’t find what you’re looking for?
Fill out this form to inquire about our custom protein services!
Inquire about our Custom Services >>


































 Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit! Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
Request a FREE Sample of our FcRn Binding Kit!
 Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.  Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
Limited Edition Golden Llama is here! Check out how you can get one.
 Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!  Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
Request a FREE sample of our GMP products!
> The Complement System, An Innate Immunity Station 
The Complement System occupies a unique position among early cellular sensors, acting directly on the surface of triggering cells or substances to coordinate downstream cellular humoral immune responses. This makes this system a critical part of the immune cascade, contributing to both innate immune responses, including:
As a global regulator of immunity and tissue homeostasis, the Complement System has become an interesting, yet complex pharmacological target, contributing a network that contributes to pathogenesis in various inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases, as well as, cancers.
Overall, the Complement-targeted therapies has been a very active field in recent years. Potent complement inhibitors are now available and increasingly used in approved and off-label indications that demonstrate the therapeutic potential of complement control.
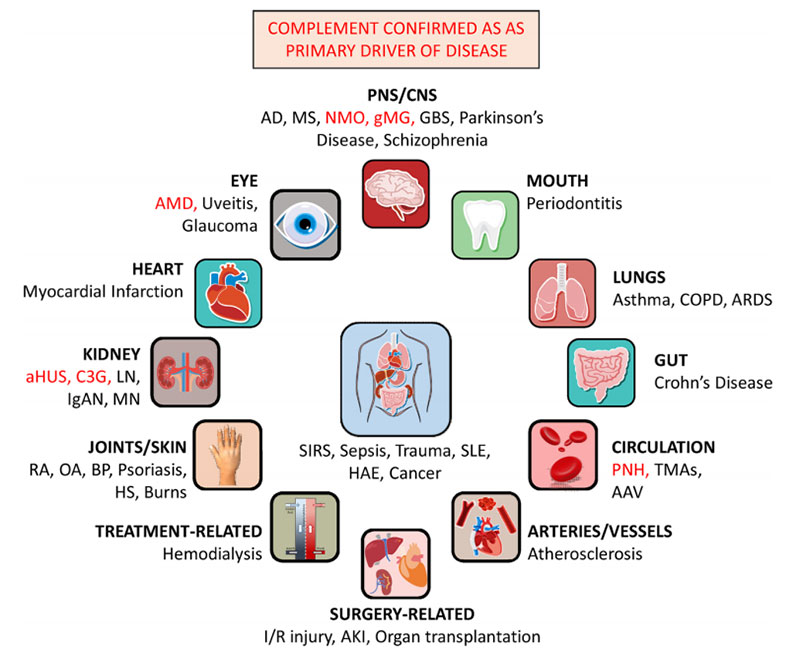
Complement activation is implicated in numerous diseases
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.07.030
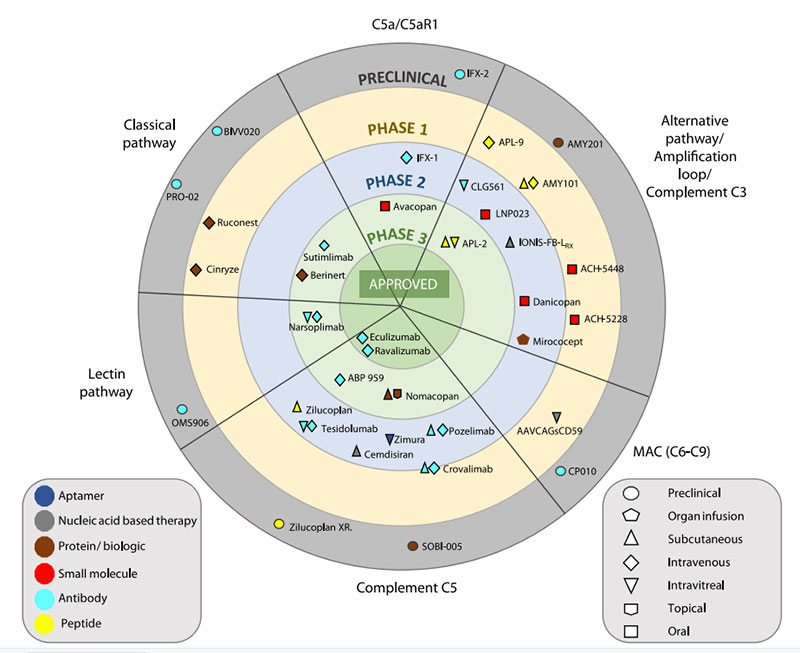
Anti-complement drugs currently in clinical development
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2019.07.030
A better understanding of the complement's structure, function, and biological role will support our complement-based understanding to contribute to treating inflammation, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancers. Complement-targeted drugs that intervene at the signaling cascade level can help to better tailor therapeutic strategies and allow such strategies to be applied to a wider range of indications. To assist with research h into the Complement system, ACROBiosystems has developed a series of recombinant complement proteins expressed by HEK293 Cells, including C2, C3, C5, C5a and complement factor D (CFD).
![]() Comprehensive catalog of Complement products are available
Comprehensive catalog of Complement products are available
![]() High purity and structural homogeneity verified by SDS-PAGE and SEC-MALS
High purity and structural homogeneity verified by SDS-PAGE and SEC-MALS
![]() Native conformation, various species, free protocols available
Native conformation, various species, free protocols available
![]() High biological activity verified by ELISA and cell-based assay
High biological activity verified by ELISA and cell-based assay
| Molecule | Cat. No. | Species | Product Description | Preorder/Order |
|---|
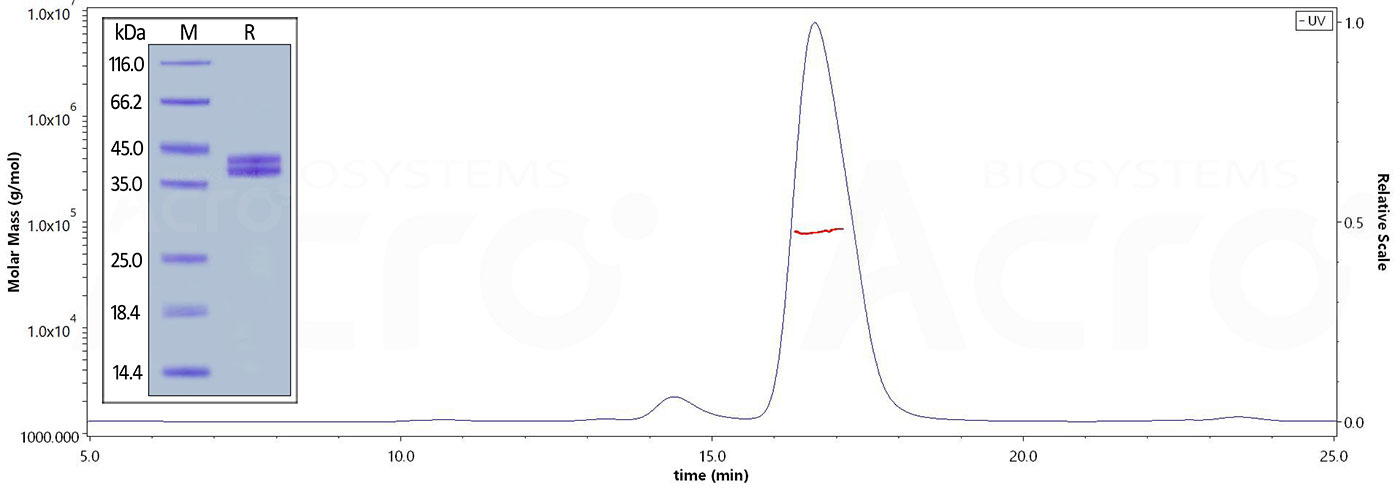
The purity of Human Complement C5a, Fc Tag (Cat. No. C5A-H525a) is more than 90% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 80-90 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
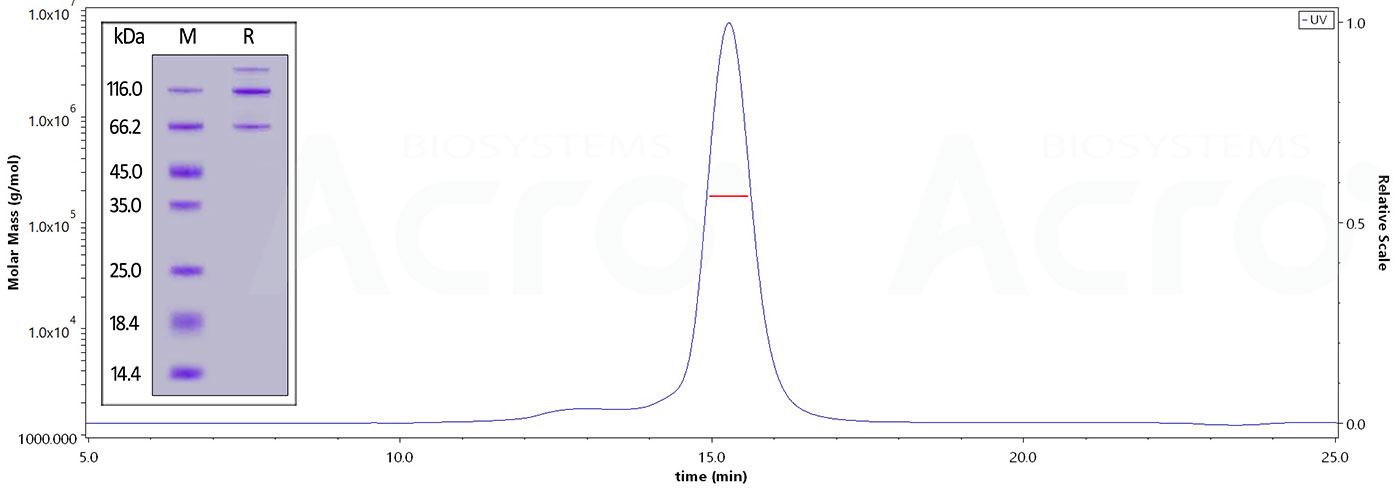
The purity of Cynomolgus Complement C3, His Tag (Cat. No. CO3-C52H5) is more than 95% and the molecular weight of this protein is around 168-205 kDa verified by SEC-MALS.
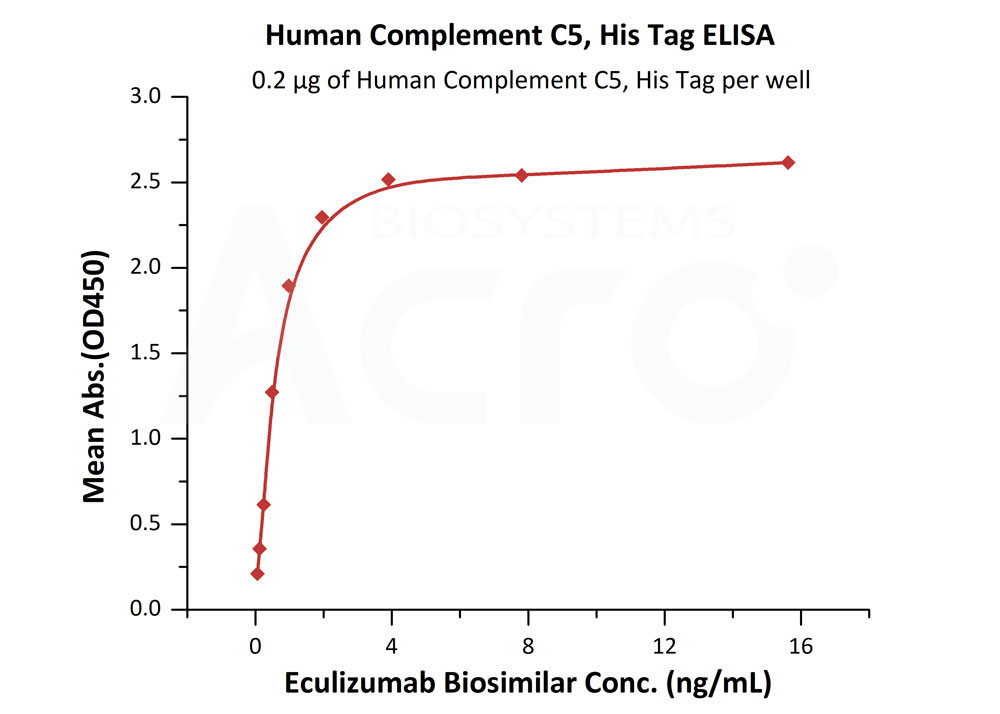
Immobilized Human Complement C5, His Tag (Cat. No. CO5-H52Ha) at 2 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Eculizumab Biosimilar with a linear range of 0.1-4 ng/mL (Routinely tested).
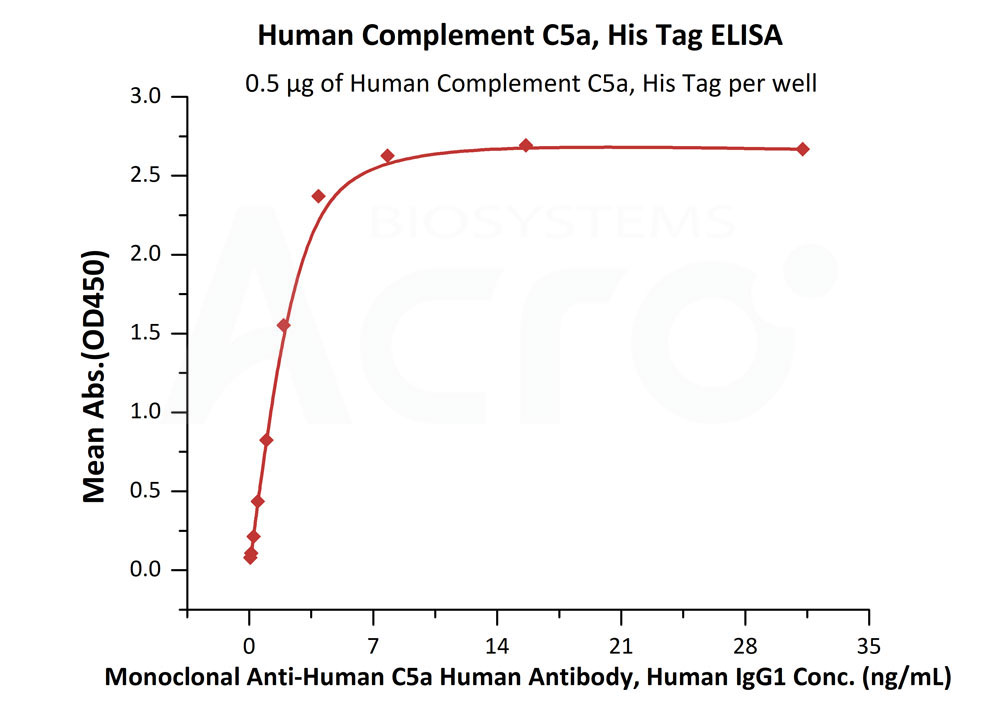
Immobilized Human Complement C5a, His Tag (Cat. No. C5A-H51H9) at 5 μg/mL (100 μL/well) can bind Monoclonal Anti-Human C5a Human Antibody, Human IgG1 with a linear range of 0.1-4 ng/ml (QC tested).
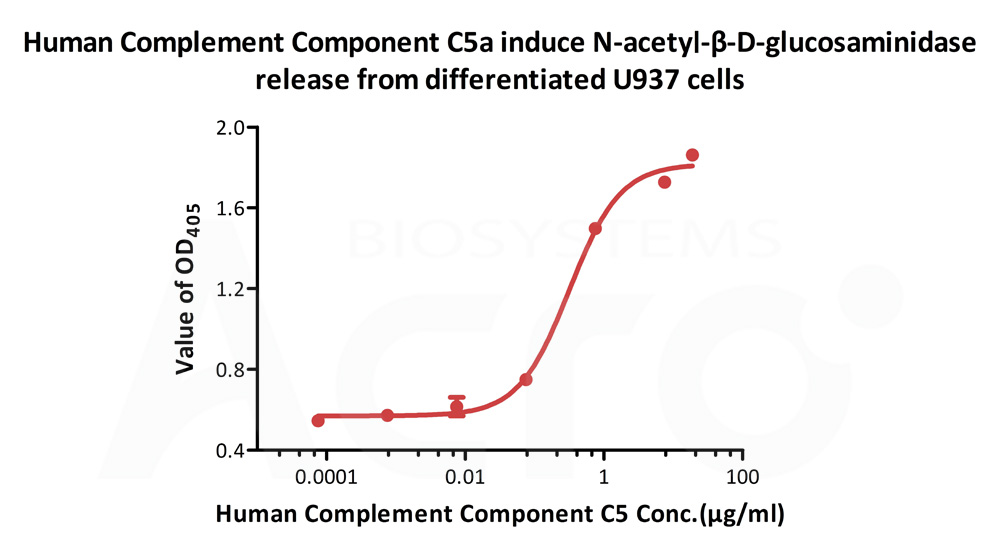
Human Complement C5a, Tag Free (Cat. No. C5A-H5116) induce N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase release from differentiated U937 cells. The ED50 for this effect is 0.215-0.323 μg/mL (Routinely tested).
> [Inspiring Target] Therapeutic Potential of Complement in Inflammation, Cancer, and COVID-19
1. King B C, Blom A M. Intracellular complement: Evidence, definitions, controversies, and solutions[J]. Immunological Reviews, 2023, 313(1): 104-119.
2. Zelek W M, Xie L, Morgan B P, et al. Compendium of current complement therapeutics[J]. Molecular immunology, 2019, 114: 341-352.
3. Lubbers R, Van Essen M F, Van Kooten C, et al. Production of complement components by cells of the immune system[J]. Clinical & Experimental Immunology, 2017, 188(2): 183-194.
4. Ricklin D, Lambris J D. New milestones ahead in complement-targeted therapy[C]//Seminars in immunology. Academic Press, 2016, 28(3): 208-222.
This web search service is supported by Google Inc.








